by Claire Dwoskin
Children’s Medical Safety Research Institute
It would probably surprise few people to hear that food allergies are increasingly common in U.S. children and around the world. According to one public health website, food allergies in children aged 0-17 in the U.S. increased by 50% from 1997 to 2011.
Although food allergies are now so widespread as to have become almost normalized, it is important to realize that millions of American children and adults suffer from severe rapid-onset allergic reactions that can be life-threatening. Foods represent the most common cause of anaphylaxis among children and adolescents. The United Kingdom has witnessed a 700% increase in hospital admissions for anaphylaxis and a 500% increase in admissions for food allergy since 1990.
The question that few are asking is why life-threatening food allergies have become so alarmingly pervasive. A 2015 open access case report by Vinu Arumugham in the Journal of Developing Drugs, entitled “Evidence that Food Proteins in Vaccines Cause the Development of Food Allergies and Its Implications for Vaccine Policy,” persuasively argues that allergens in vaccines—and specifically food proteins—may be the elephant in the room.
Historical Perspective
As Arumugham points out, scientists have known for over 100 years that injecting proteins into humans or animals causes immune system sensitization to those proteins. And, since the 1940s, researchers have confirmed that food proteins in vaccines can induce allergy in vaccine recipients. Arumugham is not the first to bring the vaccine-allergy link to the public’s attention. Heather Fraser makes a powerful case for the role of vaccines in precipitating peanut allergies in her 2011 book, The Peanut Allergy Epidemic: What’s Causing It and How to Stop It. In that fascinating book, Fraser notes that mass allergic phenomena (called “serum sickness” at the time) first emerged at the close of the nineteenth century in tandem with mass vaccination.
Allergens in Vaccines
What food proteins are found in vaccines? The list includes ovalbumin, casein, gelatin, and soy. As Arumugham ascertained, however, synthetic vaccine ingredients such as polysorbate 80 and sorbitol also are sourced from food items, including coconut, palm, sunflower, wheat, and corn. Arumugham observes that it is likely impossible to fully eliminate residual allergen proteins deriving from these sources. Moreover, it takes very low-level exposure to food proteins to cause allergic sensitization.
Synergy with aluminum-based adjuvants
A more subtle and troubling point is that the aluminum adjuvants contained in many vaccines augment the food proteins’ immunogenicity (a substance’s ability to provoke an immune response). When numerous food proteins and adjuvants get injected in one sitting, as is the case when multiple shots are administered simultaneously, the probability of sensitization greatly increases.
Implications
The Institute of Medicine admits that food proteins in vaccines “occasionally induce…sensitization…and subsequent hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis.” Despite this knowledge, the allergen content in vaccines is entirely unregulated. No safe level or limits have ever been established or enforced for the allergens contained in vaccines.
In this context, it is hard to disagree with Arumugham’s suggested solutions. The most obvious response—one that would likely alleviate much suffering—is to remove food proteins and aluminum compounds from vaccines as soon as possible. To decrease the odds of allergic sensitization, it also makes sense to adopt the precaution of decelerating the vaccine schedule and administering one vaccine at a time. In the interim, the link between vaccines and food allergies needs to be openly discussed so that the public can be more fully informed about vaccine risks.
Download this FREE Summary of Studies from Vaccines & Autoimmunity.
Read the full article at CMSRI.org.
Leaving a lucrative career as a nephrologist (kidney doctor), Dr. Suzanne Humphries is now free to actually help cure people.
In this autobiography she explains why good doctors are constrained within the current corrupt medical system from practicing real, ethical medicine.
One of the sane voices when it comes to examining the science behind modern-day vaccines, no pro-vaccine extremist doctors have ever dared to debate her in public.
Medical Doctors Opposed to Forced Vaccinations – Should Their Views be Silenced?
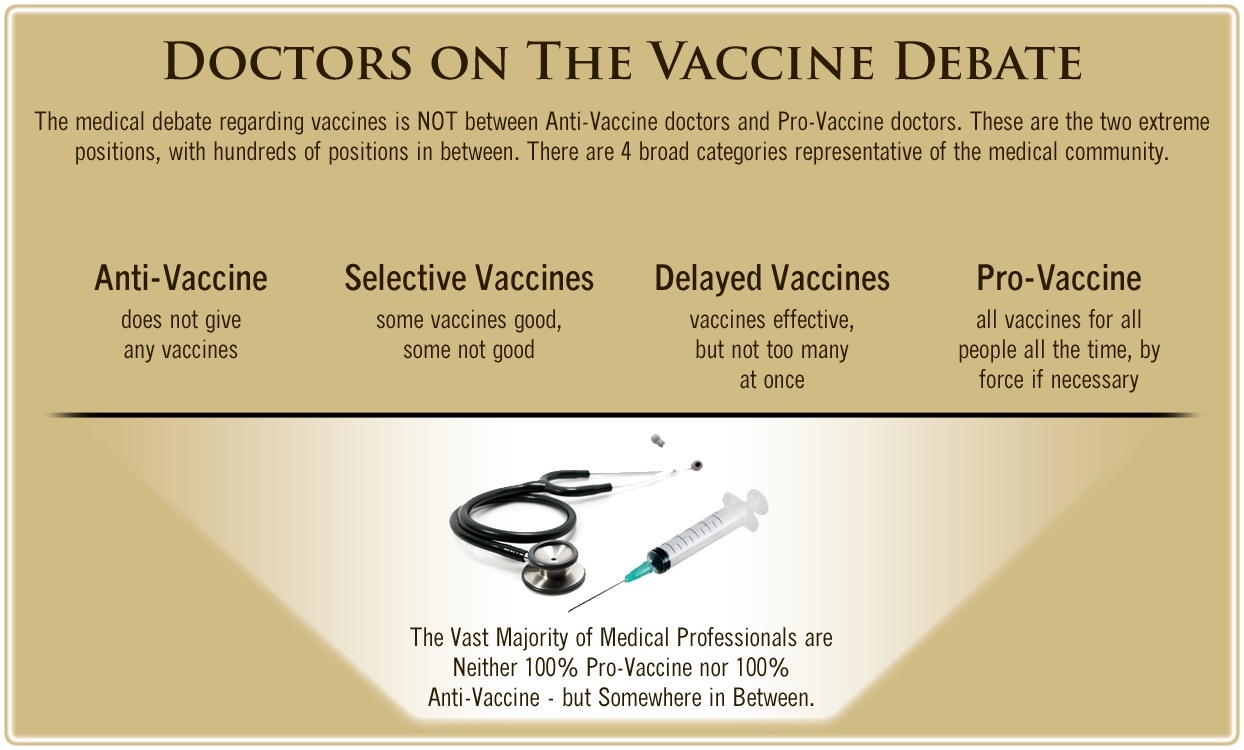
One of the biggest myths being propagated in the compliant mainstream media today is that doctors are either pro-vaccine or anti-vaccine, and that the anti-vaccine doctors are all “quacks.”
However, nothing could be further from the truth in the vaccine debate. Doctors are not unified at all on their positions regarding “the science” of vaccines, nor are they unified in the position of removing informed consent to a medical procedure like vaccines.
The two most extreme positions are those doctors who are 100% against vaccines and do not administer them at all, and those doctors that believe that ALL vaccines are safe and effective for ALL people, ALL the time, by force if necessary.
Very few doctors fall into either of these two extremist positions, and yet it is the extreme pro-vaccine position that is presented by the U.S. Government and mainstream media as being the dominant position of the medical field.
In between these two extreme views, however, is where the vast majority of doctors practicing today would probably categorize their position. Many doctors who consider themselves “pro-vaccine,” for example, do not believe that every single vaccine is appropriate for every single individual.
Many doctors recommend a “delayed” vaccine schedule for some patients, and not always the recommended one-size-fits-all CDC childhood schedule. Other doctors choose to recommend vaccines based on the actual science and merit of each vaccine, recommending some, while determining that others are not worth the risk for children, such as the suspect seasonal flu shot.
These doctors who do not hold extreme positions would be opposed to government-mandated vaccinations and the removal of all parental exemptions.
In this article, I am going to summarize the many doctors today who do not take the most extremist pro-vaccine position, which is probably not held by very many doctors at all, in spite of what the pharmaceutical industry, the federal government, and the mainstream media would like the public to believe.






Leave a Reply