The lawfirm of Maglio Christopher & Toale, P.A. announced earlier this month (July, 2018) that they had negotiated a $101 million dollar settlement for an infant who suffered a severe reaction to the Measles Mumps Rubella (MMR) vaccine.
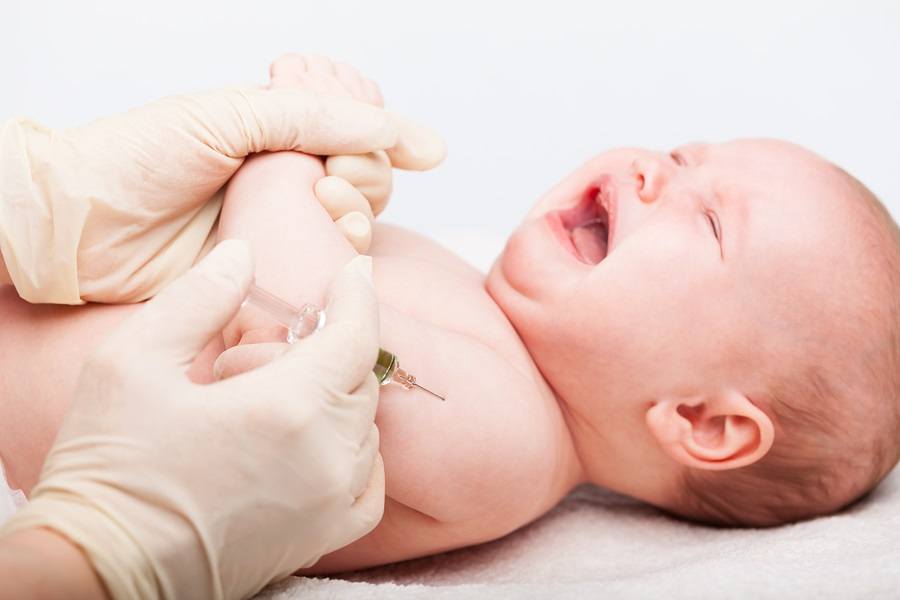
A one-year-old healthy baby girl, who was already walking and climbing, received vaccinations for Measles Mumps Rubella (MMR), Hepatitis A, Haemophilus Influenzae type B (Hib), Prevnar (pneumonia), and Varicella (chickenpox) on February 13, 2013.
That evening, the mother noticed the baby was irritable and feverish.
After a call to the pediatrician, the doctor advised Mom to give her Tylenol and Benadryl. The fever continued for several days, and on the evening before the baby’s scheduled pediatrician visit, the baby began having severe seizures.
She was rushed to the emergency room. She went into cardiac and respiratory arrest, and doctors placed her on a ventilator.
The seizures and cardiac arrest left the baby with a severe brain injury, encephalopathy, cortical vision impairment, truncal hypotonia (low muscle tone), and kidney failure.
After months of treatment at the hospital, the baby finally went home, but her disabilities required specialized medical care and supervision around the clock for the rest of her life.
The $101 million dollar settlement will pay for the child’s constant high-level medical care for the rest of her life. The family received a lump sum of $1 million dollars to cover the immediate costs of medical bills and expenses. The rest will be paid out through an annuity over the child’s lifetime.
Don't expect to read this story in the Big Pharma-sponsored corporate "mainstream" media, where the official doctrine is that vaccines are "safe and effective."